A Symmetric Image Cipher Using Wave Perturbations
Introduction
Inspired by the natural ripple-like phenomenon that distorts a reflection on a water surface, this paper introduces a new symmetric image cipher using wave perturbations to shuffle images in an n dimensional (n D) space. Its strong diffusion and confusion properties are ensured by pseudo-random wavefronts and additional salts and peppers bits. To improve the image cipher׳s confusion and diffusion properties, it introduced the additional pseudo-noise and diffusion chaining. These improvements require a low computational cost but guarantee a uniform distribution for 0-bits and 1-bits. Simulation results have shown that the proposed cipher is a fast solution to protect image contents, outperforms several existing methods, and has higher randomness and more evenly distributed pixels.
Main results
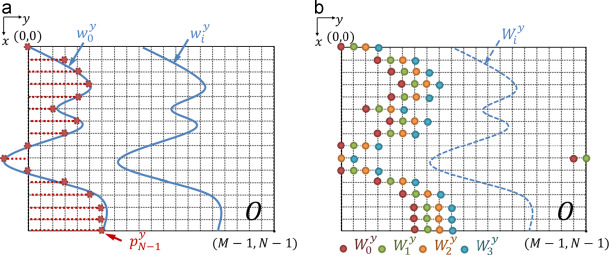 |
| Discretization of wave perturbations for digital images. (a) Continuous wavefronts (blue curves) and discrete zero-wavefront (stems), and (b) discrete wavefronts. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure caption, the reader is referred to the web version of this paper.) |
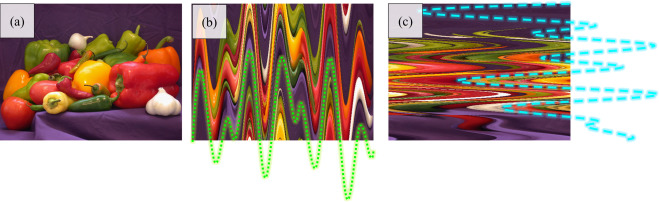 |
| Image scrambling using wave perturbations. (a) Original peppers image. The IS results using a wave propagating along the (b) x-axis and (c) y-axis directions. |
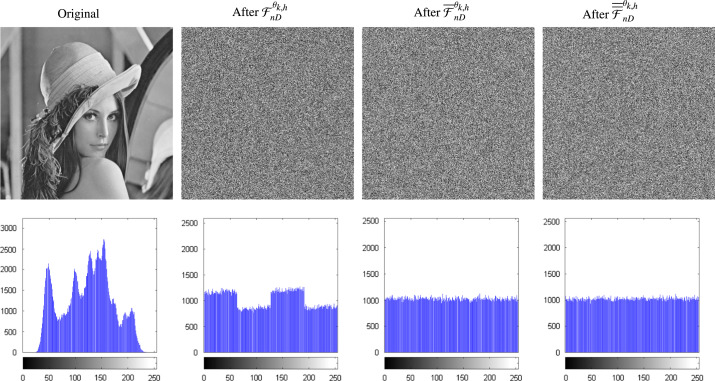 |
| n D-WPIC effects on image Lenna. |
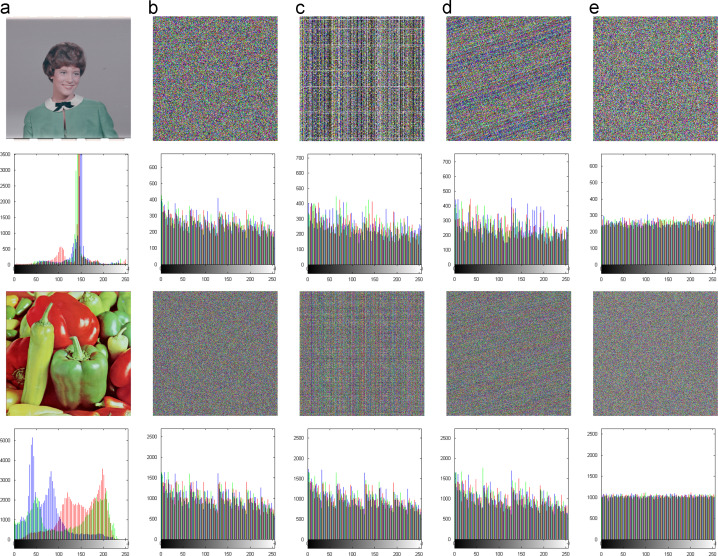 |
| Image scrambling using various methods (images in the 1st and 3rd rows are sizes of 256×256×3 and 512×512×3, respectively). (a) original images and their histograms. Scrambled images and their histograms using the (b) classic method, (c) Ye׳s method, (d) Fu׳s method, and (e) proposed n D-WPIC. |
Reference:
Yue Wu, Yicong Zhou, Sos Agaian, and Joseph P. Noonan, “A Symmetric Image Cipher using Wave Perturbations,” Signal Processing, vol. 102, pp. 122–131, 2014.